What is Gynecologic Cancer & Its Types

Table of Contents
- What is Gynecologic Cancer?
- Types of Gynecologic Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
- Causes of Cervical Cancer
- Uterine Cancer
- Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
- Causes of Uterine Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
- Causes of Ovarian Cancer
- Vaginal Cancer
- Symptoms of Vaginal Cancer
- Causes of Vaginal Cancer
- Vulvar Cancer
- Symptoms of Cancer of the vulva
- Causes of Cancer of the vulva
- Risk Factors of Gynaecological Cancer
- Tips to Prevent Gynaecological Cancer
- Gynaecological Cancer and Female Infertility
- Gynecologic Cancer Treatment
- Conclusion
- FAQs:
What is Gynecologic Cancer?
- Cancer can be simply explained as an uncontrolled division of cells in the body, which can be fatal. This type of growth can begin in any part of your body.
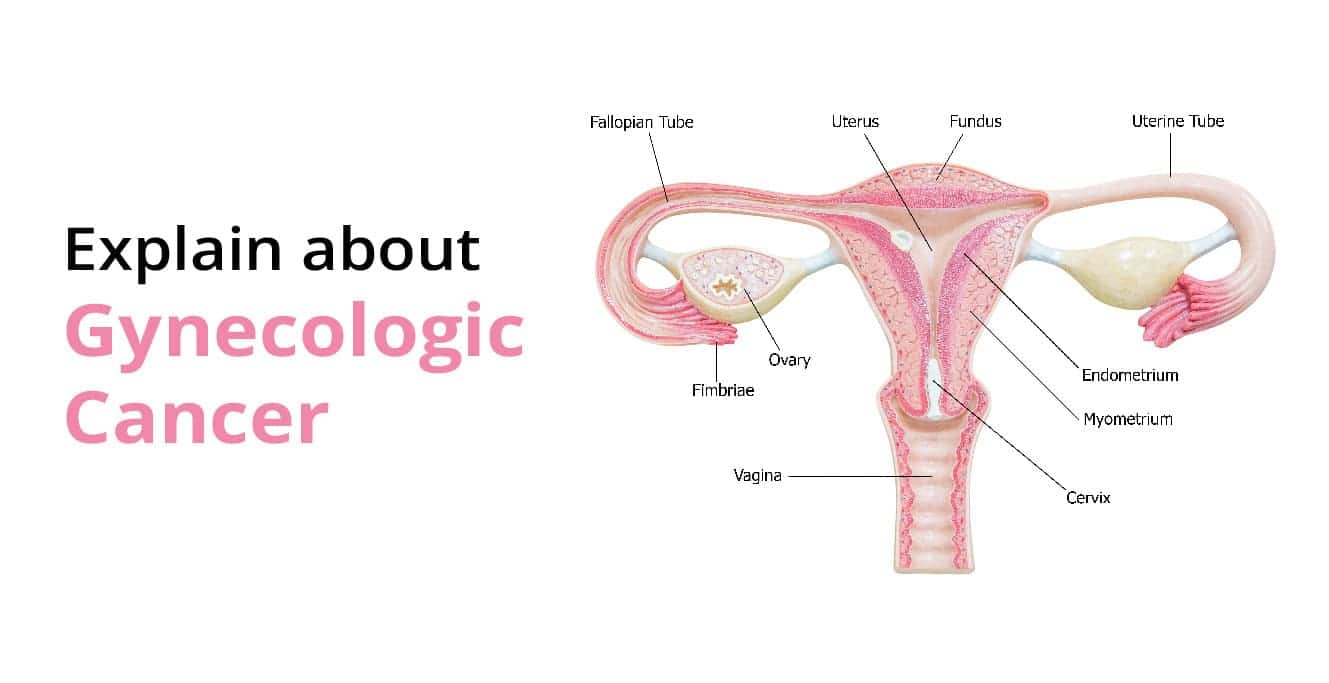
- Gynecologic cancer is a disease that develops in the reproductive organs of a woman. Uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, and cancers of external genital organs are all included in the term gynecologic cancer.
- The female reproductive system consists of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, vagina, and vulva. Cancer in women can affect any part of the reproductive system, and the symptoms are experienced according to the location of the cancer. These cancers are one of the major causes of death in women in India and worldwide.
- Of all the types, cervical and ovarian cancers are seen most frequently.
Types of Gynecologic Cancer
Gynecologic cancer is classified as per the reproductive organ it arises from. Five types of cancers are seen in the female reproductive system. These are as follows:
Cervical Cancer
This cancer starts in the cervix, the narrow passage at the lower end of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It often develops slowly from pre-cancerous changes and is primarily caused by persistent infection with certain types of HPV (Human Papillomavirus). It is the only gynecologic cancer with an effective screening test, the Pap smear.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Here is an overview of stage-wise cervical cancer symptoms. Consult your gynaecologist if you notice any of these symptoms.
Stage 1 Cervical Cancer Symptoms
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding (after sex, between periods, or after menopause)
- Watery or blood-tinged vaginal discharge
- Mild pelvic pain or discomfort during sex
Stage 2 Cervical Cancer Symptoms
- Irregular Periods (Heavier or longer menstrual bleeding)
- Pain during sex
- Pelvic pain or backache
- Foul-smelling discharge
Stage 3 Cervical Cancer Symptoms
- Trouble urinating or blood in urine
- Swelling in the legs (due to lymph blockage)
- Persistent pelvic or lower back pain
- Constipation or difficulty passing stools
Stage 4 Cervical Cancer Symptoms
- Severe pelvic or abdominal pain
- Blood in urine or stool
- Weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite
- Breathlessness (if lungs are involved)
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted disease, is considered the cause of almost every cervical cancer. The HPV infection causes cellular changes in the cervix, leading to abnormal cell growth, called dysplasia, which is a precancerous stage.
If caught early, this type of gynecologic cancer is treatable.
Uterine Cancer
Found in the uterus, where a baby grows during pregnancy, this cancer is most commonly endometrial cancer, which begins in the uterine lining. Less commonly, it may develop in the muscle or other tissues of the uterus (uterine sarcoma), which tends to be more aggressive. Postmenopausal bleeding is often the first warning sign.
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer symptoms include vaginal bleeding after menopause, painful intercourse, difficulty passing urine, pain in the abdomen, etc. However, these symptoms can also be due to some other cause. You need to see your gynaecologist to understand the reason for these symptoms.
Causes of Uterine Cancer
Being obese is a common risk factor for uterine cancer. Age, having a family member with uterine cancer, polycystic ovarian syndrome, never having children, medicines used for breast cancer, etc., are some of the other risk factors that predispose you to uterine cancer.
Ovarian Cancer
This cancer begins in the ovaries, which produce hormones and release eggs during a woman’s reproductive years. It can be hard to detect early because symptoms are vague (bloating, pelvic pain). They have different types, of which epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common and aggressive type of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer symptoms are usually vague or resemble many other conditions. You can have bloating, pain in the lower abdomen, feeling full quickly after food intake, constipation, unexplained weight gain or weight loss, etc. But if these symptoms are unusual and do not seem to go away, you must see a gynaecological specialist to get it diagnosed.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The likelihood of developing this gynecologic cancer increases with age. Those with one or more family members having ovarian or breast cancer, obese women, smokers, and those who never had children are more prone to develop ovarian cancer.
Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer arises in the vaginal lining, which is the muscular canal leading from the cervix to the vulva. It is quite rare and typically affects women over 60. Risk factors include HPV infection and a history of cervical cancer or abnormal cervical cells.
Symptoms of Vaginal Cancer
People with vaginal cancer can experience foul-smelling vaginal discharge, abnormal vaginal bleeding, painful intercourse, or pain after sexual intercourse. Consult your gynaecologist to diagnose the condition if you have these symptoms.
Causes of Vaginal Cancer
The most common cause of vaginal cancer is being infected with human papillomavirus. Age and a weak immune system are other risk factors.
Vulvar Cancer
This cancer occurs on the external part of the female genitals, the vulva, including the labia and clitoris. It is rare and usually slow-growing. Often seen in older women, early signs may include persistent itching, changes in skin colour, or a lump or sore that doesn’t heal.
Symptoms of Cancer of the vulva
Symptoms of cancer of the vulva include a lump on or around the vulva, itching in the vulva, burning or pain in the vulva, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin region, and any mole that has changed in shape or colour etc. If you are experiencing such symptoms, you need to consult gynaecological specialists.
Causes of Cancer of the vulva
Human papillomavirus, age, smoking, weak immunity, etc., are some risk factors that increase your chances of getting this gynecologic cancer.
Risk Factors of Gynaecological Cancer
Here are the key risk factors of gynaecological cancers (cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, vulvar):
- Age: The risk of gynaecological cancer increases with age, especially after 50 may be due to cellular ageing, weakened immune system, hormonal changes, etc.
- Family history: If there is a family history of gynaecological cancer, especially ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer, this increases the risk.
- Genetic mutations: These include BRCA1, BRCA2, and Lynch syndrome.
- HPV infection: It is a key reaosn for cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers.
- Obesity: Increases the risk of endometrial (uterine) cancer.
- Smoking: It increases the risk of cervical and vulvar cancers.
- Early menstruation or late menopause: Risk is increased due to prolonged oestrogen exposure.
- Weakened immune system: Less ability to fight HPV and abnormal cells due to a weak immune system increases the risk.
Tips to Prevent Gynaecological Cancer
- Get regular screenings: Routine Pap smears and HPV tests help detect early changes in cervical cells before they turn cancerous.
- Take the HPV vaccine: Getting vaccinated in adolescence or early adulthood can protect against high-risk HPV strains that cause most cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to higher levels of oestrogen, which increases the risk of endometrial (uterine) cancer.
- Avoid smoking: Tobacco use weakens the immune system and is directly associated with a higher risk of cervical and vulvar cancers.
- Practice safe sex: Using protection and limiting sexual partners reduces the risk of HPV and other infections that can lead to cancer.
- Manage diabetes and hormonal conditions: Conditions like diabetes and PCOS can disrupt hormonal balance, which may raise the risk of uterine and ovarian cancers.
- Know your family history: If close relatives have had ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer, discuss genetic testing or early screening options with your doctor.
- Exercise regularly and eat a balanced diet: A healthy lifestyle boosts immune function, reduces inflammation, and helps regulate hormone levels.
Gynaecological Cancer and Female Infertility
Here is how gynaecological cancer can impact female infertility:
- Cancer location and type: Cancers of the ovaries, uterus, cervix, or fallopian tubes can directly affect the organs needed for pregnancy.
- Treatment side effects: Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation can damage reproductive organs, reduce hormone production, or cause early menopause.
- Surgical removal: Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) or oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries) makes pregnancy impossible naturally.
- Scarring or blocked tubes: Radiation or surgery may lead to scarring in the reproductive tract, affecting egg movement or implantation.
Fertility Preservation Options:
- Egg or embryo freezing before treatment
- Ovarian tissue freezing in certain cases
- Ovarian shielding during radiation therapy
- Fertility-sparing surgeries if cancer is detected early and confined
Gynecologic Cancer Treatment
The primary goal of gynecologic cancer treatment is the complete removal of the cancer or shrinking it. The treatment modalities involve surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
The treatment plan is derived as per the individual patient’s disease condition, the type of gynecologic cancer one suffers from, and its stage.
Some types require surgery and chemotherapy, some need surgery and radiation, while some types of gynecologic cancers need all three modes.
Surgery
Considered the most beneficial treatment option for certain gynecologic cancers, surgery can be minimally invasive surgery, gynecologic robotic surgery, partial removal of the female reproductive system or complete removal, and other options.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves administering medicines that kill the tumour inside the body. These medicines are either injected into the body or given by mouth by gynaecological specialists to destroy the cancer cells in your body.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy involves X-rays or other beams to destroy uncontrollably growing cancer cells. It can be used as a stand-alone therapy or in combination with other modes of treatment for gynecologic cancer.
Conclusion
Gynecologic cancer is a real problem among women, especially cervical and ovarian cancer. However, timely intervention and treatment can help before it becomes complicated. If you think you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should talk to our specialists at Birla Fertility & IVF, where you will get comprehensive care and quality treatment.
Book your appointment today
FAQs:
- Which is the most curable gynecologic cancer?
Ans: The most curable gynecologic cancer is endometrial cancer, arising from the inner lining of the uterus. This type of cancer is usually seen after the age of 55.
- What are the 5 gynaecological cancers?
Ans: The 5 gynecologic cancers are cervical cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, vaginal cancer, and vulval cancer.
- What are the symptoms of gynaecological cancer?
Ans: Some common symptoms of gynecologic cancer are abnormal vaginal bleeding, painful intercourse, lower abdominal pain and fullness, unexplained weight loss, a lump in the genital area, and swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
- What is the most common gynaecological cancer?
Ans: The most common gynecologic cancers are cervical and ovarian cancer. Cervical cancer develops in the cervix of the uterus, while ovarian cancer develops in the ovaries. The most common cause of cervical cancer is HPV, a sexually transmitted disease.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers















