Dysmenorrhea: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment

Table of Contents
Have you ever had period pain so intense that it disrupted your entire day? While some level of discomfort during menstruation is common, for many women, the pain can be far more severe. This condition is known as Dysmenorrhoea. A medical term for extremely painful periods caused by uterine contractions. In other words, severely painful menstrual periods and cramps.
There exist two Dysmenorrhoea types, namely, primary and secondary dysmenorrhoea:
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea refers to painful menstrual periods that are very common. It occurs without any organic cause in your teenage years and twenties.
- Secondary Dysmenorrhoea refers to painful menses that are less common and happen in your thirties and forties. It occurs because of an underlying cause, particularly some reproductive disorders or diseases.
Pathophysiology of Dysmenorrhoea
The pathophysiology of Dysmenorrhoea is primarily linked to increased production of prostaglandins, particularly prostaglandin F2α, in the endometrium during the luteal phase. High prostaglandin levels cause hypercontractility of the uterus, vasoconstriction, and reduced uterine blood flow, resulting in ischaemia and pain.
These contractions are often more forceful and less coordinated than in normal cycles, which further contributes to cramping sensations. Additionally, inflammatory mediators such as leukotrienes play a role in amplifying uterine contractions and sensitising nerve endings, intensifying the perception of pain.
Difference Between Amenorrhoea and Dysmenorrhoea
You must have heard about amenorrhoea as well, but do not confuse it with dysmenorrhoea. Even though both conditions affect the menstruation cycle and fertility, they require distinctly different diagnostic approaches. Let’s see how they both different from each other:
| Amenorrhoea | Dysmenorrhoea |
| Amenorrhoea is the absence of menstruation | Dysmenorrhoea refers to painful menstruation |
| Classified as primary (when menstruation has not begun by age 15–16) or secondary (when periods stop for three or more months in a previously menstruating woman) | Classified as primary (without pelvic disease, caused by excess prostaglandins) and secondary (due to underlying pathology such as endometriosis or fibroids). |
| Causes may include hormonal imbalances, stress, eating disorders, excessive exercise, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or structural abnormalities of the reproductive tract. | Causes may include conditions like endometriosis, adenomyosis, fibroids, PCOS, or pelvic infections. |
Symptoms of Dysmenorrhea
Severe menstrual pain and cramps are the most common symptoms shared by both types of Dysmenorrhoea.
Pain in primary dysmenorrhea begins a day or two before the start of your menstrual periods and ends within 12- 36 hours. In secondary dysmenorrhea, pain starts several days before the beginning of your periods and lasts even after the cycle for the month is complete.
The symptoms of the two types of dysmenorrhea are separately listed below.
Primary Dysmenorrhea Symptoms
- Lower back pain and pelvic pain
- Pain in thighs and hips
- Headache and fatigue
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Irritation and anxiety
- Eruption of acne
Secondary Dysmenorrhea Symptoms
- Sudden extreme abdominal pain
- Chills and fever
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Pain or vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Heavy period bleeding with blood clots
- Low backache and pelvic pain
- Irregularity in periods
- Painful urination and bowel movements
Also Read: Ovary Size for Pregnancy
Causes of Dysmenorrhea
There are several causal factors of dysmenorrhea. Dysmenorrhea causes are distinct for each type, as mentioned below:
Primary Dysmenorrhea Causes
Your uterus contracts – to divest its lining – throughout your menstrual cycle. Research reveals that a hormone-like chemical known as prostaglandin activates this contraction of your uterus.
Before your period starts, there is a drop in your progesterone level. As a result, prostaglandin increases, and your uterus contracts more forcefully during menstruation.
Extreme uterine contraction can make it press against adjacent blood vessels and obstruct the flow of oxygen to your muscular tissues. When a muscle temporarily runs out of oxygen, you will experience severe pain (primary dysmenorrhea).
Secondary Dysmenorrhea Causes
Secondary dysmenorrhea is mainly caused by specific reproductive disorders and diseases, such as:
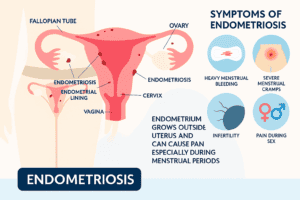
- Endometriosis: In this condition, the tissue that functions somewhat like the lining of the uterus grows outside it – on the fallopian tubes, pelvis, and ovaries. This tissue bleeds when you are on your menstrual period; it causes severe menstrual pain, heavy bleeding, and inflammation.

- Adenomyosis: In this ailment, the tissue that borders your uterus starts to integrate with your uterus’s muscular wall. This increases the size of your uterus and causes extreme abdominal pain and bleeding.
- Fibroids: These are benign tumours of the uterus. They create inflammation of the uterus and put pressure on your spine and hence cause intense pain.
- Cervical stenosis: In this condition, the opening of your uterus is very narrow and obstructs menstrual flow. This leads to a surge in pressure within the uterus, and as a result, you experience overwhelming menstrual pain.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): It refers to an infection caused by bacteria or sexually transmitted infections. It begins in the uterus and circulates to other reproductive parts. It causes scarring in the uterine lining and predisposes you to develop secondary dysmenorrhea.
- Intrauterine device (IUD): It is a contraceptive tool that blocks implantation by irritating your endometrium lining. IUD increases your risk of suffering from PID and secondary dysmenorrhea.
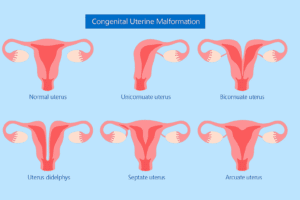
- Uterine abnormalities: These refer to malformations of the uterus and are responsible for causing severe pain during your menses.
Treatment of Dysmenorrhea
Though dysmenorrhea can be very painful, it comes with a silver lining – it is treatable.
So, if you wish to know more about dysmenorrhea treatment methods, keep reading, as they are separately written below for the two distinct types.
Primary Dysmenorrhea Treatment
In case you suffer from primary dysmenorrhea, you can follow any one of the following treatment methods to get relief from the overwhelming menstrual pain.
- Medication
According to a study, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as flurbiprofen, ibuprofen, and tiaprofenic acid are very effective in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. They reduce the severity of dysmenorrhoea by blocking the production of prostaglandin.
Moreover, another study reveals oral contraceptive pills are effective in curtailing intense pain during menses by limiting the growth of the uterine lining, reducing the production of prostaglandin and inhibiting ovulation.
You can take either of these medications at the start of your menses but only after consulting a doctor.
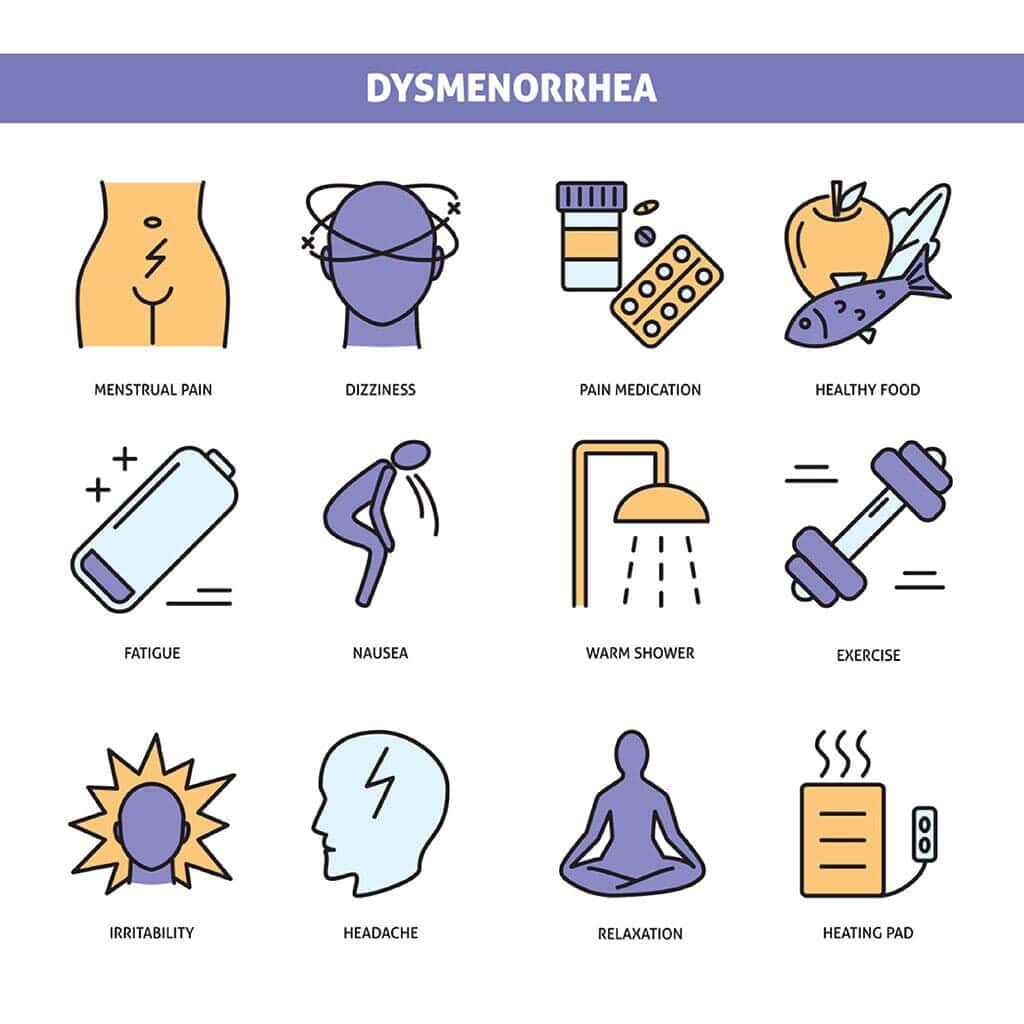
- Lifestyle and diet modifications
To successfully decrease dysmenorrhea, you can implement the following changes in your lifestyle and diet:
- Eat a healthy diet rich in vitamins like vitamin E and minerals
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy lifestyle
- Avoid alcohol, sugar and caffeine intake
- Avoid having dairy products and smoking
- Take warm showers or baths during menses
- Use a heating pad to relax your uterus muscles or massage your abdomen
- Practice yoga and breathing techniques
- Rest more when on your periods
- Alternative therapies
Besides the above methods, you can try out these alternative therapies to treat primary dysmenorrhea.
A study reports that high-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is effective in reducing the severity of dysmenorrhea. It sends out electrical currents and interferes with the pain signals that your nerves send to your brain.
Moreover, practising acupuncture and acupressure also helps. They involve pressing specific nerve points and aid in decreasing the intensity of dysmenorrhea.
Secondary Dysmenorrhea Treatment
The treatment of secondary dysmenorrhea depends on the causal factor of secondary dysmenorrhea.
Generally, the treatment involves hormone therapy. For instance, if your causal factor is endometriosis, a study reveals that progestin-only pills are effective for treatment. They work by weakening the endometrial lining and inhibiting ovulation which causes you to have less frequent menstrual periods.
Additionally, surgery is often used for the treatment of secondary dysmenorrhea. It usually involves laparoscopic surgery, uterine nerve ablation, and different types of hysterectomy. Surgery can also entail the repair of anomalies in your uterus.
Types of Dysmenorrhoea Based on Pain Pattern
- Spasmodic Dysmenorrhoea– It is caused due to excessive uterine contractions due to high prostaglandin levels, leading to sharp, cramping pain at the onset of menstruation.
- Congestive Dysmenorrhoea– Pain develops gradually before menstruation due to pelvic congestion and persists throughout the cycle, often dull and heavy.
- Endometriosis-Related Dysmenorrhoea- Results from ectopic endometrial tissue causing inflammation and adhesions, leading to severe, progressive menstrual pain.
- Ovulatory Dysmenorrhoea– Mid-cycle pain (mittelschmerz) occurs during ovulation due to follicle rupture and peritoneal irritation.
- Membranous Dysmenorrhoea– Severe pain caused by the shedding of the endometrium as large casts or membranes, which is rare but very distressing.
- IUD-Associated Dysmenorrhoea– Linked to the presence of an intrauterine device, often due to increased prostaglandin release and uterine irritation.
Conclusion
Do you experience excruciating pain and cramps during menstruation? Do you feel like you suffer from dysmenorrhea?
If the answer to both questions is affirmative – you can consult the experienced fertility specialists and doctors at Birla Fertility and IVF. It is a top-notch fertility clinic with cutting-edge technologies for testing. The clinic also has an exceptional success rate.
To confirm your suspicion of dysmenorrhea, visit your nearest Birla Fertility and IVF centre or book an appointment with Dr. Muskaan Chhabra.
FAQs:
What is the best treatment for dysmenorrhea?
The best treatment for dysmenorrhea depends on your causal factor and type of dysmenorrhea.
In the case of primary dysmenorrhea, the above-stated methods – taking medication, making lifestyle and diet-related changes and following alternative therapies – are quite effective for treatment.
In the case of secondary dysmenorrhea, the best treatment depends on your causal factor and usually involves either hormone therapy or surgery.
What is the first-line treatment for dysmenorrhea?
The first-line treatment for dysmenorrhea comprises taking NSAIDs such as flurbiprofen, ibuprofen, etc. They work by obstructing prostaglandin’s production. And, in turn, significantly decrease the severity of dysmenorrhea.
How to treat Dysmenorrhoea naturally?
Natural treatments for Dysmenorrhoea include applying heat, practising yoga or exercise, eating an anti-inflammatory diet (rich in omega-3s, magnesium, and herbal teas), and managing stress through relaxation techniques. These methods help relax uterine muscles, improve blood flow, and naturally reduce menstrual pain without medication.
How painful is Dysmenorrhoea?
Dysmenorrhoea pain can range from mild cramps to severe, debilitating pelvic pain that interferes with daily activities. In severe cases, it may cause nausea, fatigue, or dizziness alongside intense menstrual cramps.
Is Dysmenorrhoea genetic?
Yes, genetics can play a role, as women with a family history of painful periods are more likely to experience Dysmenorrhoea. Inherited conditions like endometriosis or adenomyosis may also contribute to its occurrence.
How to avoid Dysmenorrhoea?
Regular exercise, a healthy diet, stress management, and avoiding smoking or excess caffeine may help prevent Dysmenorrhoea. Early treatment of underlying conditions and maintaining hormonal balance also reduces the risk.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers Select City
Select City 
















