Can a Bicornuate Uterus (Double Uterus) Affect Fertility?

Table of Contents
- Types of Bicornuate Uterus
- Cause of a Bicornuate Uterus
- What Should I Do if I Have a Bicornuate Uterus?
- Bicornuate Uterus vs. Septate Uterus
- Symptoms of Bicornuate Uterus
- How does Bicornuate Uterus Affect Pregnancy?
- Treatment of Bicornuate Uterus
- Success Rate of Bicornuate Uterus Pregnancy
- How a Bicornuate Uterus Affects Twin Pregnancies:
A bicornuate uterus, also known as “double uterus”, is a rare condition that usually has no symptoms. Women do not even know that they have a bicornuate uterus until they try to conceive. Even though it sounds complex, it is simply a difference in how the uterus is shaped. However, for some women, it can raise concerns about fertility, pregnancy, and delivery.
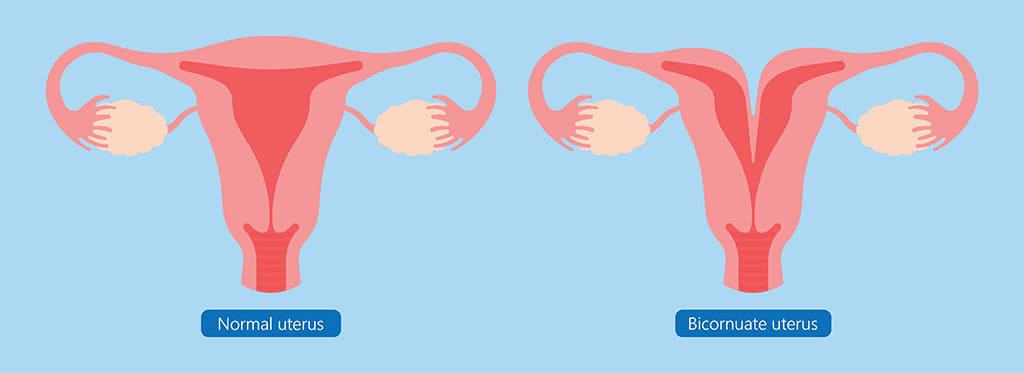
How does this anomaly look? It is characterised by a heart-shaped structure with a deep indentation at the top. A bicornuate uterus is partially divided into two distinct cavities, which can affect pregnancy outcomes.
If you’ve been diagnosed with a uterine anomaly, it is natural to be overwhelmed and worried. Hence, we bring you this blog to understand what a bicornuate uterus is and how it can affect your fertility. Knowing the nitty-gritty can help you navigate this journey with more confidence and clarity.
Prevalence:
About 0.1% to 0.5% of women have a bicornuate uterus, which makes it a somewhat uncommon disorder. Nonetheless, it is a crucial topic for women’s health because of its effect on fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Let’s explore its causes, symptoms, and potential impact on reproductive health, along with available treatment options and strategies.
Types of Bicornuate Uterus
A bicornuate uterus can be classified into two main types based on the degree of separation:
- Bicornuate bicollis uterus, also known as a complete bicornuate uterus
- Bicornuate unicollis uterus, also known as a partial bicornuate uterus
|
Type of Uterus |
Structure |
Cavity Division |
Cervix |
|
Normal uterus |
The uterus has a single pear-shaped cavity. |
No division (single cavity). |
Single cervix. |
|
Complete bicornuate uterus |
The uterus is fully divided into two separate cavities, forming two distinct horns. |
Fully divided into two cavities. |
Two cervices may be present. |
|
Partial bicornuate uterus |
The uterus is partially divided, with the upper portion separated while the lower part remains connected. |
Partially divided, mainly at the top. |
Single cervix (typically |
Cause of a Bicornuate Uterus
Now comes the question: what are the reasons behind the cause of a bicornuate uterus?
Specialists and researchers have not entirely understood the cause behind it, but it is said to be the outcome of incomplete fusion of the Müllerian ducts during foetal development. This generally happens between the 10th and 20th week of pregnancy.
Note: Having a bicornuate uterus is not hereditary. There are no genetic or environmental factors that contribute to this anomaly.
A bicornuate septate uterus is a variant of the bicornuate uterus where the septum dividing the uterus extends down into the cervix. This condition can further complicate pregnancy and may require additional monitoring and interventions.
What Should I Do if I Have a Bicornuate Uterus?
In case you have a bicornuate uterus, do not worry. Even though they can affect fertility, it doesn’t mean that you can’t have a healthy pregnancy.
However, the first thing to do is confirm the diagnosis through imaging tests. Your doctor will recommend that you either go for an ultrasound or an MRI, according to your medical history. Once done, you will need to consult with an expert gynaecologist or fertility specialist. They will help you understand what kind of treatment you might need.
In many cases, the women do not need any surgery, and simple medication helps them conceive. However, there are complex cases of recurrent miscarriage and other complications that need a corrective procedure. The prenatal has to be monitored regularly in such cases, and you will need to watch for risks involving preterm labour or breech position. Staying informed, following your doctor’s advice, and scheduling timely check-ups can help you manage the condition and plan for a safe delivery.
Bicornuate Uterus vs. Septate Uterus
Both a bicornuate uterus and a septate uterus fall under the congenital uterine abnormalities. Though they have different structures and are treated differently. The bicornuate uterus has two separate cavities due to partial fusion of the Müllerian ducts. This is what gives the uterus a heart-like exterior form.
Although both bicornuate and septate uteri are congenital uterine abnormalities, they are treated differently and have different structures. A bicornuate uterus has two separate cavities due to partial fusion of the Müllerian ducts, giving it a heart-like exterior form. A fibrous or muscular septum divides the chamber inside a septate uterus, which often has a normal external shape. This distinction is significant because a modest hysteroscopic procedure can often repair a septate uterus, improving the outcome of pregnancy. Only when a bicornuate uterus causes serious reproductive issues is it treated, usually requiring more extensive surgery.
Symptoms of Bicornuate Uterus
Many women with a bicornuate uterus do not experience any noticeable symptoms. However, some common signs and symptoms may include:
- Repeated miscarriages
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Painful intercourse
- Painful periods
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other gynaecological conditions, so it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
How does Bicornuate Uterus Affect Pregnancy?
Increased Risk of Miscarriage
The presence of a septum or division in the uterus can significantly impact implantation success. The irregular shape may lead to:
-
Impaired blood supply: A divided uterus can affect blood flow to the developing foetus, which is critical for providing the necessary nutrients and oxygen for growth.
-
Challenges in uterine expansion: The abnormal structure may restrict the uterus’s ability to stretch as the foetus grows, leading to potential complications and increasing the likelihood of miscarriage.
Preterm Labour and Delivery
The unique shape of a bicornuate uterus can limit the available space for foetal growth, potentially resulting in:
-
Early contractions: The confined environment may trigger the uterus to contract prematurely, leading to preterm labour.
-
Increased likelihood of premature delivery: Studies have shown that women with a bicornuate uterus have a higher rate of preterm births compared to those with a normal uterine shape, necessitating close monitoring throughout pregnancy.
Malpresentation of the Baby
The irregular uterine shape can affect foetal positioning, which may result in:
-
Increased likelihood of breech presentation: The foetus may not have enough space to turn into the head-down position, leading to a breech birth where the baby is positioned feet-first.
-
Transverse lie: In some cases, the baby may lie sideways in the uterus, which can complicate delivery and often requires a caesarean section for safe birth.
While a bicornuate uterus can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, research suggests that close monitoring and proper care will show positive outcomes. Globally bicornuate uterus pregnancy success rate is around 56%.
Treatment of Bicornuate Uterus
There are ways to manage a bicornuate uterus, which involves a comprehensive approach. It helps ensure that the pregnancy is healthy. Let’s see what it all involves:
- Proper Monitoring- Women who have this anomaly need to be monitored closely during pregnancy. This includes regular ultrasound and prenatal visits to help monitor the baby’s growth and positioning in the uterus.
- Cerclage Placement: There are cases of preterm labour in these conditions, which is also called a short cervix. It is when a cerclage is placed to prevent premature birth.
- Foetal Positioning: There are techniques, such as the external cephalic version, that can be used to make sure that the baby is in the head-down position for a safe delivery.
- Surgical Treatment: For extreme cases, surgical procedures like metroplasty can be done to unify the uterus. It is important in cases where the bicornuate uterus is causing issues during pregnancy. This surgery can be done laparoscopically and requires a waiting period of at least 3 months before one attempts to conceive again. It is because after this treatment, there can be a risk of uterine rupture during labour.
Success Rate of Bicornuate Uterus Pregnancy
Despite the challenges, many women with a bicornuate uterus can have successful pregnancies. The success rate is influenced by several factors, including:
-
Degree of uterine malformation: This will directly impact the success rate of the pregnancy.
-
Partial bicornuate uterus: Women with a partial bicornuate uterus typically have a larger, more functional uterine cavity, which can support foetal growth more effectively. The presence of a septum may be less pronounced, allowing for better blood supply and implantation, often translates to a higher likelihood of success.
-
Complete bicornuate uterus: Here the division of the uterus can limit space for the developing foetus, potentially leading to complications such as foetal growth restriction, increased risk of malpresentation, and a higher chance of miscarriage.
-
-
Timely Natal Care: Regular prenatal visits enable doctors to closely monitor both the mother and the foetus. Early detection of any complications can facilitate prompt interventions, significantly enhancing pregnancy outcomes. Additional ultrasounds and assessments help track foetal position and growth.
-
Individual health factors: A woman’s health plays a crucial role in her pregnancy outcomes. Some key factors are
-
Existing health problems: Conditions such as obesity, diabetes, or hypertension can complicate pregnancy, impacting success rates.
-
Age: Women under 35 typically have higher fertility rates and better outcomes compared to older women, as fertility declines with age.
-
Lifestyle choices: Healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress, can positively impact fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
-
A study published in the Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology found that women with bicornuate uterus who underwent laparoscopic metroplasty had a significant improvement in reproductive outcomes:
| Outcome | Before Surgery | After Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnancy rate | 20.8% | 80.8% |
| Live birth rate | 0% | 73.1% |
| Miscarriage rate | 100% | 11.5% |
| Preterm delivery rate | N/A | 15.4% |
These findings highlight the potential benefits of surgical intervention in improving pregnancy outcomes for women with bicornuate uterus.
How a Bicornuate Uterus Affects Twin Pregnancies:
- Higher Risk of Miscarriage: Women with a bicornuate uterus are at a higher risk of miscarriage, especially during twin pregnancies, due to the abnormal shape and reduced space in the uterus. This can affect the implantation and development of both embryos.
- Preterm Labor: A bicornuate uterus may cause preterm labor or early delivery, particularly in multiple pregnancies like twins, due to the limited space for fetal growth.
- Fetal Malpresentation: In a twin pregnancy with a bicornuate uterus, one or both babies may present in abnormal positions (like breech) because of the restricted space in each uterine horn.
- Increased Risk of Complications: Other complications, such as placental abnormalities, low birth weight, and premature rupture of membranes, can also arise in a bicornuate uterus with twins.
Word From an Expert:
While a bicornuate uterus can present challenges during pregnancy, it’s important to remember that many women with this condition go on to have successful pregnancies and healthy babies. The key is to work closely with your healthcare provider, who can provide the necessary monitoring, support, and interventions to optimise your chances of a positive outcome. ~ Dr. Prachi Benera
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers Select City
Select City